Learn about various types of heart failure with this simple infographic!
Some topics you will learn in this infographic:
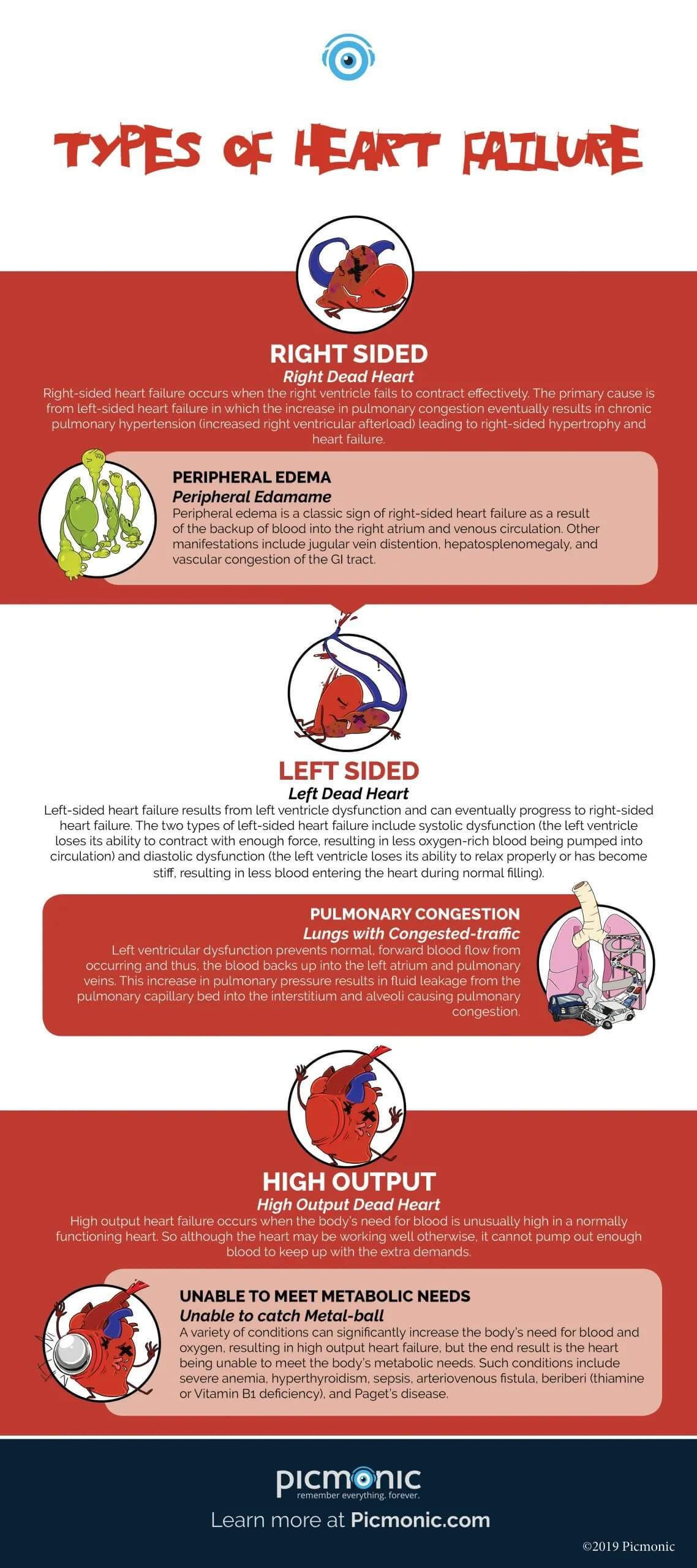
Left Side:
Left-sided heart failure results from left ventricle dysfunction and can eventually progress to right-sided heart failure. The two types of left-sided heart failure include systolic dysfunction (the left ventricle loses its ability to contract with enough force, resulting in less oxygen-rich blood being pumped into circulation) and diastolic dysfunction (the left ventricle loses its ability to relax properly or has become stiff, resulting in less blood entering the heart during normal filling).
Pulmonary Congestion:
Left ventricular dysfunction prevents normal, forward blood flow from occurring and thus, the blood backs up into the left atrium and pulmonary veins. This increase in pulmonary pressure results in fluid leakage from the pulmonary capillary bed into the interstitium and alveoli causing pulmonary congestion.
Peripheral Edema:
Peripheral edema is a classic sign of right-sided heart failure as a result of the backup of blood into the right atrium and venous circulation. Other manifestations include jugular vein distention, hepatosplenomegaly, and vascular congestion of the GI tract.
Unable To Meet Metabolic Needs:
A variety of conditions can significantly increase the body’s need for blood and oxygen, resulting in high output heart failure, but the end result is the heart being unable to meet the body’s metabolic needs. Such conditions include severe anemia, hyperthyroidism, sepsis, arteriovenous fistula, beriberi (thiamine or Vitamin B1 deficiency), and Paget’s disease.