In the realm of emergency medical care, the ability to perform Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) can make the difference between life and death. In this article, we will embark on a comprehensive journey through the essential principles, skills and strategies that allow healthcare providers to deliver life saving interventions in critical cardiac situations.
An infographic detailing the steps of Advanced Cardiac Life Support.
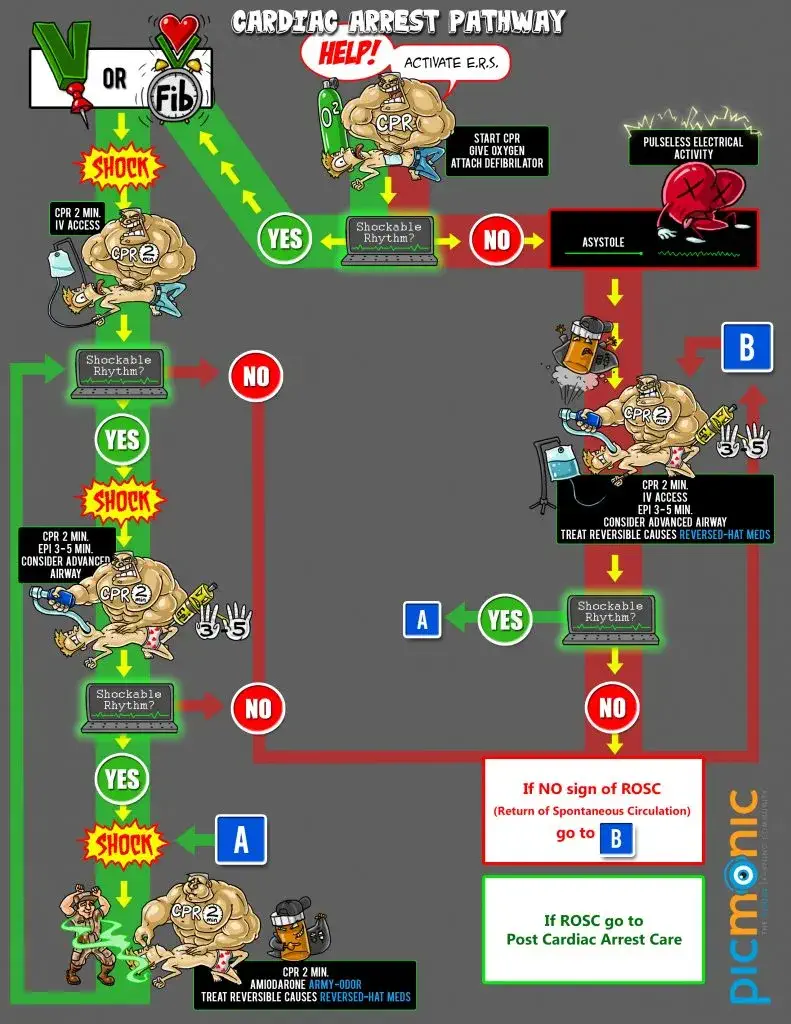
The specific steps in ACLS can vary depending on the patient’s condition and the healthcare providers assessment, but here’s a general outline of the key components and steps involved:
1. Assessment and Recognition:
- Determine the responsiveness of the patient.
- Check for signs of breathing or abnormal breathing
- Activate the emergency response system
2. CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation)
- Initiate chest compressions at the appropriate rate and depth
- Coordinate ventilation with chest compressions as needed
- Continue CPR until an automated external defibrillator (AED) is available
3. Defibrillation
- If a defibrillator is available, apply as soon as possible
- Analyze the patients heart rhythm and deliver appropriate shocks as indicated
4. Airway Management
- Establish and maintain an open airway
- Consider the use of advanced airway devices as needed
5. Breathing Support
- Provide artificial ventilation as necessary using a bag valve or other appropriate devices
- Ensure proper ventilation rate and volume
6. Medication Administration
- Administer medication as indicated based on the patient’s specific condition
- Follow dosing guidelines and consider the use of advanced life support drugs when necessary
7. Cardiac Monitoring
- Continuously monitor the patient’s cardiac rhythm and vital signs
- Adjust treatment strategies in response to changes in the patient’s condition
8. Post-Resuscitation Care
- Initiate therapeutic hypothermia in eligible patients to protect brain function
- Optimize oxygenation, ventilation and blood pressure
- Address the underlying cause of the cardiac event and initiate appropriate interventions