This Infographic will walk you through everything you need to know regarding Metabolism Cycles.
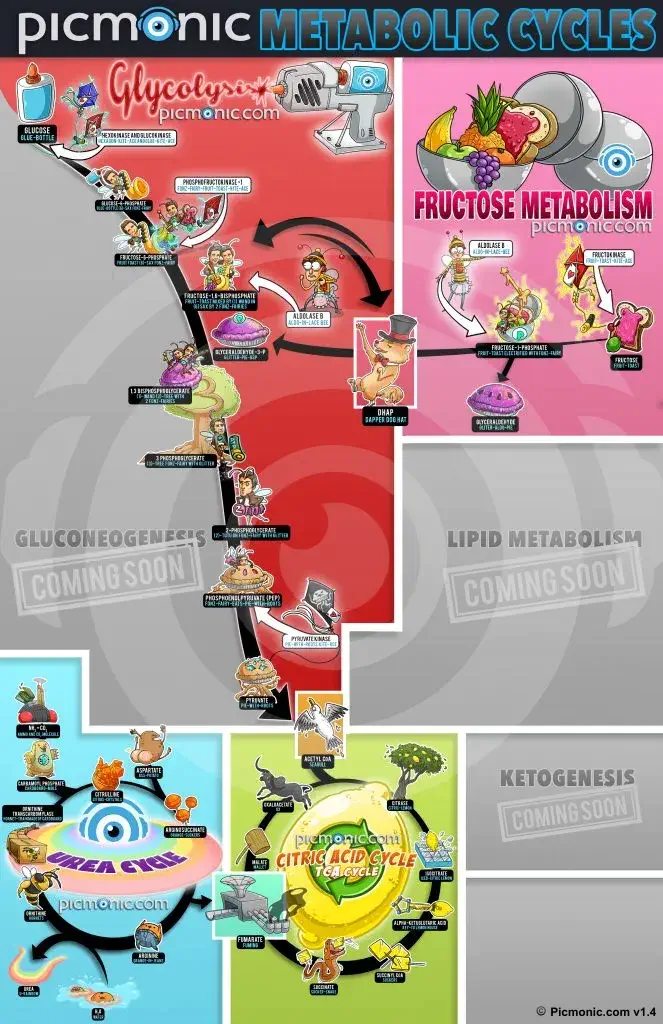
Some topics you will learn in this infographic:
Produces Insulin from non-Carbohydrate Substrates:
During nighttime or prolonged fasts, there is less glucose readily available for the tissues of the body. However, the high-glucose requirements of certain tissues such as the brain and kidneys remains. To meet these requirements, the liver begins producing glucose from a variety of substrates. These include pyruvate (from glycolysis), lactate (from anaerobic metabolism), glycerol (from triglycerides), and various glucogenic amino acids.
Fructose:
Fructose is a ketogenic monosaccharide that is broken down to form components for gluconeogenesis or glycolysis.
Carbamoyl Phosphate:
Carbamoyl phosphate enters the urea cycle as a substrate for ornithine transcarbamylase, which converts this substrate and ornithine into citrulline.
To learn more, get started with a free Picmonic account.