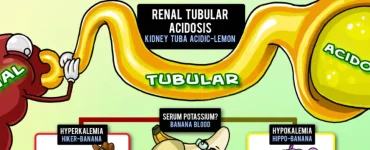
Getting ready for Step 1?
We know the hard work, late nights, and intense struggle that goes into the preparation for Step 1. It takes a special kind of dedication to put in the work to get yourself fully prepared.
We want everyone to have the best opportunity to CRUSH Step 1 this summer.
So what does that mean?
We’ve compiled a list of 20 medicine Picmonics that you have to check out before taking Step 1!
20 PHARM PICMONICS YOU NEED TO KNOW FOR STEP 1:

1. 1st Generation Cephalosporin
Cephalosporins are beta-lactam antibiotics that are derived from Acremonium fungus. Like other beta-lactams, these antibiotics work by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. However, they are not as susceptible to penicillinases.
2. 2nd Generation Cephalosporin
3. 3rd Generation Cephalosporin
4. 4th Generation Cephalosporin
5.  Aminopenicillin Mechanism
Aminopenicillin Mechanism
Aminopenicillins are antibiotics that belong to the penicillin family. Like penicillins, aminopenicillins are beta-lactam antibiotics, which work by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis.
6. Cephalosporin
Cephalosporins are beta-lactam antibiotics that are derived from Acremonium fungus. Like other beta-lactams, these antibiotics work by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. However, they are not as susceptible to penicillinases.
7 . Tetracycline Mechanism
. Tetracycline Mechanism
Tetracyclines are a group of broad-spectrum antibiotics named after their structure which contains a four hydrocarbon ring derivative. Drugs in this group include tetracycline, doxycycline, demeclocycline, and minocycline.
8. Direct Cholinomimetics
Direct cholinomimetics are drugs which work as agonists at muscarinic cholinoreceptors and increase parasympathetic activity.
9. Indirect Cholinomimetics
Indirect Cholinomimetics
Indirect cholinomimetics, also known as anticholinesterases, work to decrease the action of the acetylcholinesterase enzyme (which works to break down acetylcholine).
10. Anticholinergics
Anticholinergic drugs act by decreasing cholinergic transmission and are also known as muscarinic antagonists. Commonly used anticholinergic medications include Benztropine, Oxybutynin, Atropine and Scopolamine.
11.  Nonselective α Blockers
Nonselective α Blockers
Phentolamine and phenoxybenzamine are drugs which lower blood pressure by inhibiting vasoconstriction through their action at α1, while also having action at α2 receptors.
12. Octreotide
Octreotide is a long-acting somatostatin-analog with various indications. It is used acutely to help stop variceal bleeds. It is used for a wide range of hormone-secreting tumors, as this medication inhibits the secretion and activity of various endocrine hormones.
13.  Anticholinergics Continued
Anticholinergics Continued
Anticholinergic medications are used to decrease cholinergic transmission and are also referred to as muscarinic antagonists. The medication glycopyrrolate blocks muscarinic activity on airway secretions, as well as stomach acid secretions.
14. Levothyroxine
Levothyroxine is a synthetic T4 that is converted to T3 by 5’deiodinase in peripheral tissues. T3 and to a smaller degree, T4, then bind to thyroid hormone nuclear receptors in target cells to exert their effects.
15.  PTU (Propylthiouracil)/ Methimazole
PTU (Propylthiouracil)/ Methimazole
Propylthiouracil (PTU) and methimazole are two commonly used medications in patients with hyperthyroidism. Both drugs block the action of thyroid peroxidase, thus inhibiting thyroid hormone synthesis.
16. Metformin
Metformin is part of the Biguanide class of diabetic drugs. It is the first line medical treatment for diabetes mellitus type 2 and can also be used for PCOS.
17.  Clindamycin
Clindamycin
Clindamycin is a bacteriostatic antibiotic commonly used to treated infections with anaerobic bacteria. It is a bacterial protein synthesis inhibitor that binds to the 50S ribosomal subunit and inhibits ribosomal translocation, similar to macrolides.
18. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor Poisoning
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor poisoning, also known as organophosphate toxicity and cholinergic overdose, is often seen in farmers, as organophosphates are commonly found in insecticides.
19.  Epinephrine
Epinephrine
Epinephrine is a direct sympathomimetic that is used for the treatment of hypotension, anaphylaxis, and open-angle glaucoma. It is most commonly administered intravenously and is metabolized extensively by the liver prior to excretion.
20. NSAIDs
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic agents. Many drugs fall into this drug family including ibuprofen, naproxen, indomethacin, ketorolac and aspirin among many others.
Check out these 20 Picmonics covering high-yield topics to get your started using Picmonic for Medicine to study for Step 1. And don’t worry, we’ve got more where that came from. With over 1,400 videos to help you prepare and snag the Step 1 score of your dreams.
Get ready to crush Step 1!



 .
.