There’s a Picmonic for That! Mood Disorders
In behavioral & psychiatry specialties, knowing how to properly assess patients is critical. Mood disorders require precise and extensive understanding since assessments within mental health can often be very similar. When you need help remembering the specifics — there are several Picmonics for that! Check out our mnemonics for medical students now!

Bipolar Disorder Interventions
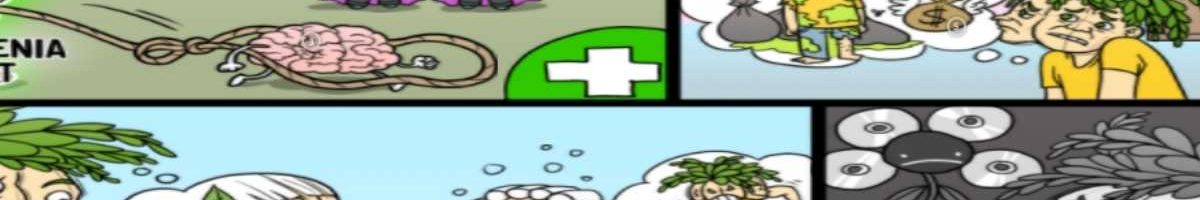
Bipolar disorder assessment is the story of the various moods and emotions of bi-polar-bear as this condition is characterized by periods of mania and periods of depression. The pathophysiology involves neurotransmitter dysregulation and genetic factors, shown by the dysregulated neurotransmitters with DNA jeans. For example, dopamine and serotonin may be elevated in manic states, while acetylcholine can be elevated in depressive states. There are 2 categories of signs and symptoms: mania and depression. Mania symptoms include an elated or euphoric mood, shown by U-flowers the bear is frolicking in. Patients may also present with nonstop physical activity, the bear running around the clock, which results in physical exhaustion and a lack of sleep. Another symptom is flight of ideas, the flight of idea lightbulbs, which is a continuous and rapid change in thought, jumping from topic to topic usually involving fragmented or unrelated ideas. It typically involves rapid speech, shown by the rapid speech bubbles. On the other hand, depressive episodes include mood changes with feelings of worthlessness, hopelessness, and despair, shown by the bear wearing moody-mask rings that are changing. The patient often presents with a sad affect, shown by the sad face. They may also experience psychomotor retardation, depicted as the brain-motor and read-tarred book. Suicidal thoughts can occur during a depressive episode, shown by the bear imagining suicidal-jumper thoughts.
So let’s review bipolar disorder assessment. It is thought to occur as a result of neurotransmitter dysregulation and genetic factors. Mania symptoms include a euphoric mood, nonstop physical activity, flights of ideas, and rapid speech. Depression symptoms involve mood changes, a sad affect, psychomotor retardation, and suicidal thoughts.
Schizophrenia Assessment
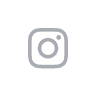
Use this Picmonic to help you recall the important facts of Schizophrenia assessment, where the sketchy-fern and the assess-man are in the pumpkin patch, being accused of smashing pumpkins. When describing the positive symptoms of schizophrenia, patients can have hallucinations, the Halloween hallucinations in the pumpkin patch. Patients can have delusions, shown by the doll-illusionists who accused and praised him at the same time. This fern was so confused, he felt like he was losing his mind, shown by the loose-lassoed brain that was trying to escape, as associative looseness is another positive symptom of schizophrenia. When it comes to the negative symptoms, patients can have a flat affect, shown as the flat face staring at the fern in the bathroom, where he went to escape. In the restroom, he thinks about how he might have poverty in his future, as poverty of thought can occur in patients. Another negative symptom is the absence of something that should be present, pictured as the absence of something that should be present in the bathroom, like hygiene products. Cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia include illogical thinking, where the fern tries to use an ill-log, thinking it will uncuff him after he’s been arrested. Another cognitive symptom is impaired judgment and memory, the impaired judge with an impaired memory who blames the fern of being guilty. Finally, schizophrenic patients can have dysphoria as an affective symptom, shown as the disc-flowers reminding the fern of his plight.
So let’s review the assessment of schizophrenia. Positive symptoms include hallucinations, delusions, and associative looseness. Negative symptoms include flat affect, poverty of thought, and the absence of something that should be present. Cognitive symptoms include illogical thinking, along with impaired judgment and memory. An affective symptom is dysphoria.